Neuropathic pain is a complex type of chronic pain that occurs due to damage or dysfunction in the nervous system. Unlike nociceptive pain (which results from tissue damage like cuts or burns), neuropathic pain is caused by the nerves themselves sending incorrect pain signals to the brain, even when there’s no actual tissue damage occurring.
Your nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (nerves throughout your body). Neuropathic pain can originate from problems in either system, affecting how pain signals are transmitted and processed.
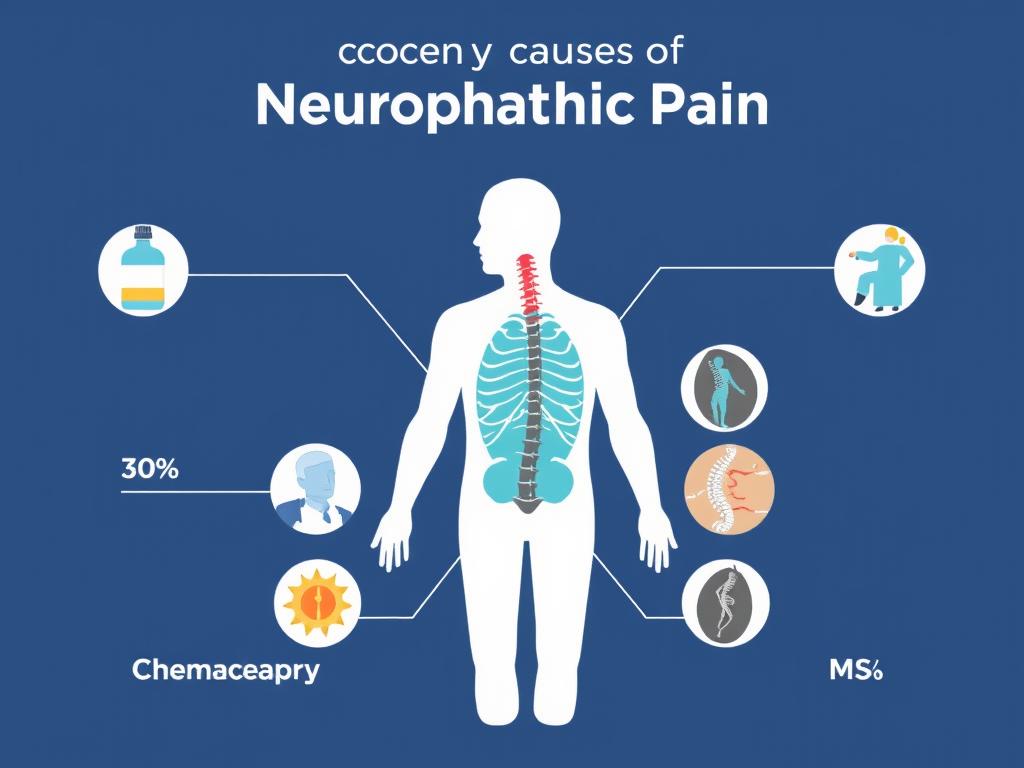
Major causes of neuropathic pain and their relative frequency
Diabetes is the leading cause of neuropathic pain, responsible for approximately 30% of cases. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage nerves over time, particularly in the feet and legs, resulting in diabetic neuropathy.
Neuropathic pain produces distinctive symptoms that differ from other types of pain. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
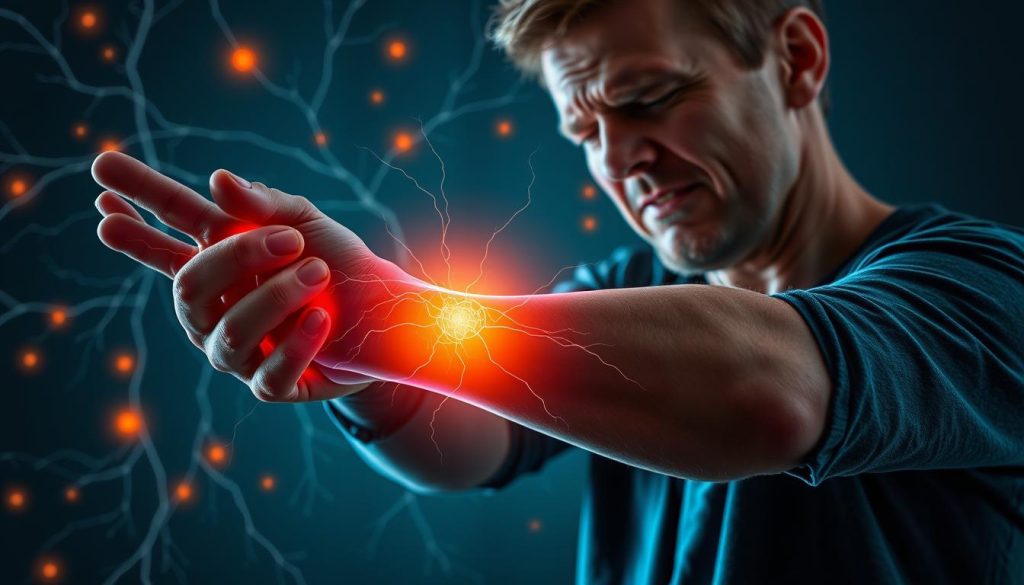

Neuropathic pain often manifests as burning, shooting, or electric shock-like sensations
Important: Neuropathic pain symptoms can vary widely between individuals and may change over time. If you experience persistent unexplained pain, numbness, or tingling, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
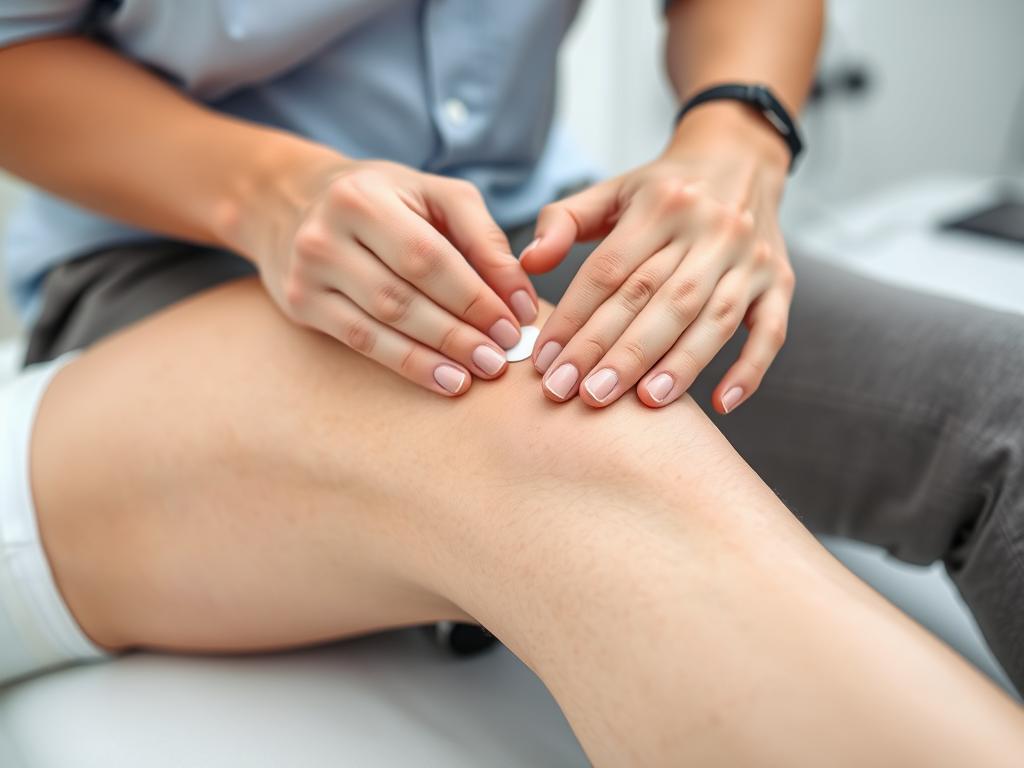
Diagnosing neuropathic pain involves a comprehensive approach to identify the underlying cause and rule out other conditions. Your healthcare provider will use several methods to make an accurate diagnosis.
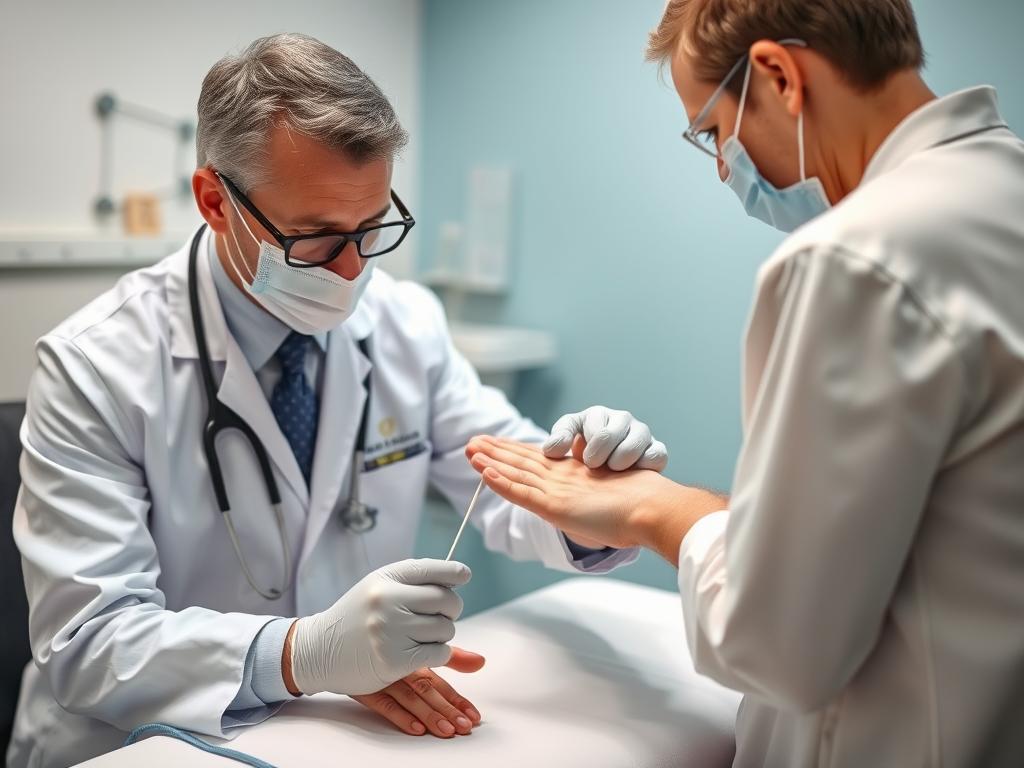
Healthcare providers use specialized tests to diagnose neuropathic pain
Your doctor will conduct a thorough review of your medical history and symptoms, followed by a physical examination to assess sensory function, muscle strength, and reflexes.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. Your healthcare provider may use standardized pain questionnaires to better understand your symptoms and their impact on your daily life.
Managing neuropathic pain often requires a multifaceted approach. Treatment strategies aim to reduce pain, improve function, and enhance quality of life. The most effective approach typically combines several treatment modalities.
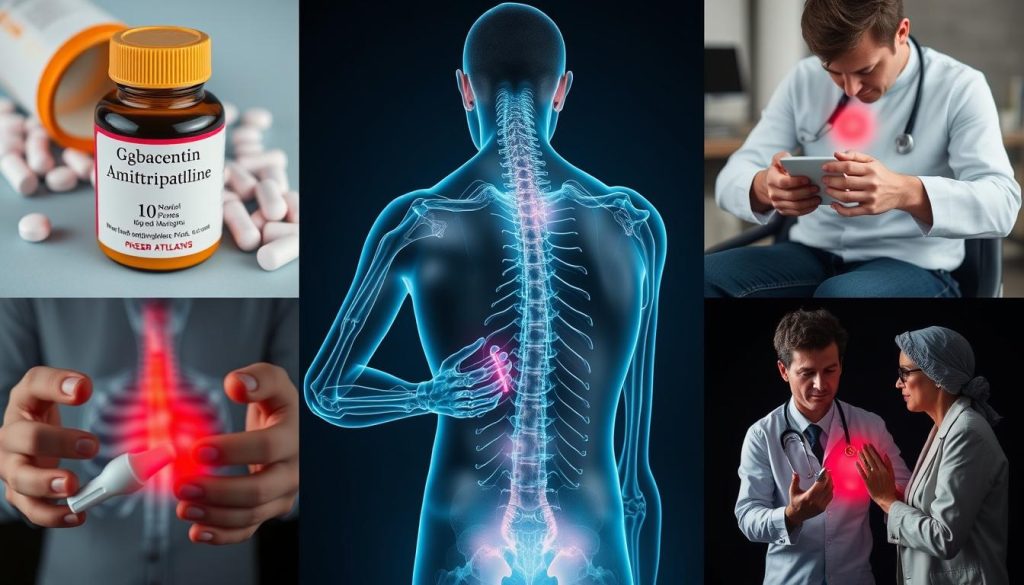
Effective management of neuropathic pain often requires multiple treatment approaches
| Medication Class | Examples | How They Work | Common Side Effects |
| Anticonvulsants | Gabapentin, Pregabalin | Stabilize abnormal nerve signals | Dizziness, drowsiness, weight gain |
| Antidepressants | Amitriptyline, Duloxetine | Modify pain transmission in the nervous system | Dry mouth, constipation, drowsiness |
| Topical Treatments | Lidocaine patches, Capsaicin cream | Block pain signals locally | Skin irritation, burning sensation |
| Pain Relievers | Tramadol, NSAIDs | Reduce pain perception | Nausea, constipation, stomach issues |

TENS units can help manage neuropathic pain by blocking pain signals
Several lifestyle changes can help manage neuropathic pain and improve overall well-being:
The field of neuropathic pain research is rapidly evolving, with promising new approaches on the horizon. These advancements offer hope for improved treatment options in the future.

Ongoing research aims to develop more effective treatments for neuropathic pain
Researchers are exploring gene therapy approaches to modify how pain signals are transmitted in the nervous system. This could potentially provide long-lasting relief for people with neuropathic pain.
New forms of neuromodulation, including dorsal root ganglion stimulation and high-frequency spinal cord stimulation, show promise for targeting specific pain pathways more effectively than traditional approaches.
Novel drug delivery systems aim to deliver pain medications directly to affected nerves while minimizing systemic side effects. This includes microscopic drug carriers and implantable devices.
Stem cell therapies and nerve growth factors are being investigated for their potential to repair damaged nerves and restore normal function in patients with neuropathic pain.
“The future of neuropathic pain treatment lies in personalized approaches that target specific mechanisms underlying each individual’s pain. We’re moving away from one-size-fits-all treatments toward precision pain medicine.”
— Journal of Pain Research, 2023
While managing neuropathic pain can be challenging, many people find ways to improve their quality of life through a combination of medical treatments and self-care strategies.
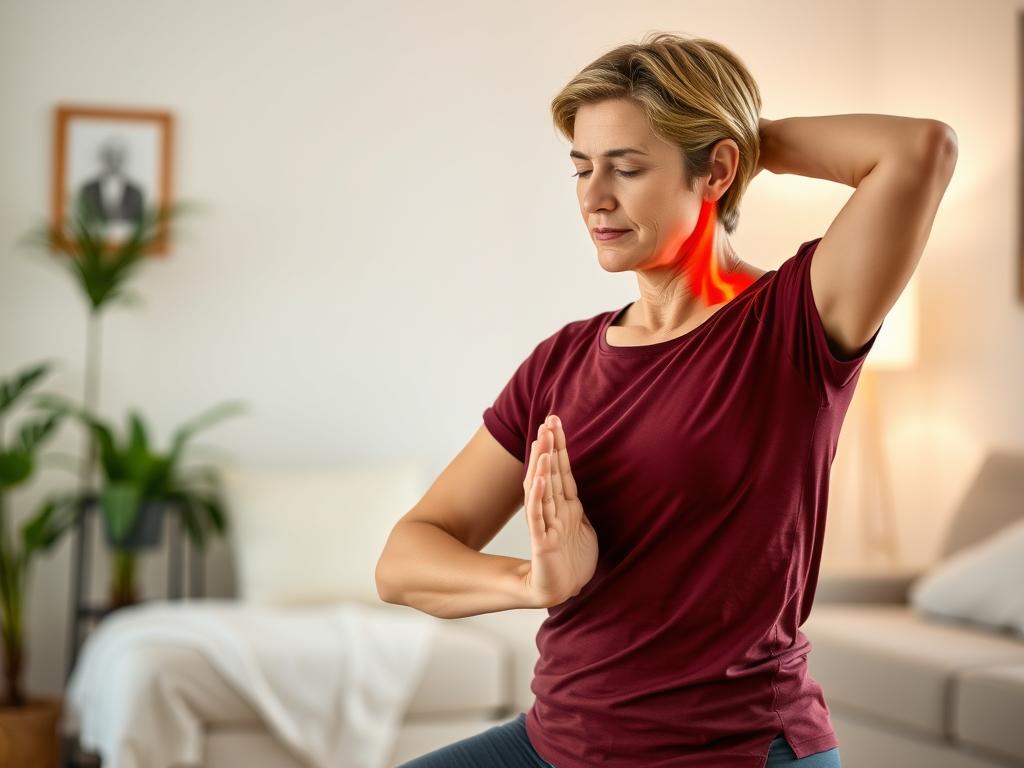

Gentle movement therapies like yoga can help manage neuropathic pain symptoms
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
Whether neuropathic pain can be completely cured depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, treating the root cause (such as controlling blood sugar in diabetes) can significantly improve or resolve symptoms. However, many forms of neuropathic pain require ongoing management rather than offering a complete cure. The goal of treatment is often to reduce pain intensity, improve function, and enhance quality of life.
Response times vary depending on the treatment and individual factors. Medications like anticonvulsants and antidepressants typically take 2-8 weeks to reach full effectiveness. Topical treatments may provide more immediate relief. Physical therapies and psychological approaches often show gradual improvement over weeks to months. It’s important to follow your treatment plan consistently and communicate with your healthcare provider about your progress.
Neuropathic pain presents unique challenges due to its complex nature and varied causes. Understanding the mechanisms behind this type of pain is crucial for effective management. While neuropathic pain can significantly impact quality of life, a comprehensive approach combining medications, physical therapies, psychological support, and lifestyle modifications can help many people find relief.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of neuropathic pain, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent worsening symptoms and improve outcomes. With ongoing advances in research and treatment approaches, the future holds promise for even better management options for those living with neuropathic pain.

Working closely with healthcare providers is essential for effective neuropathic pain management
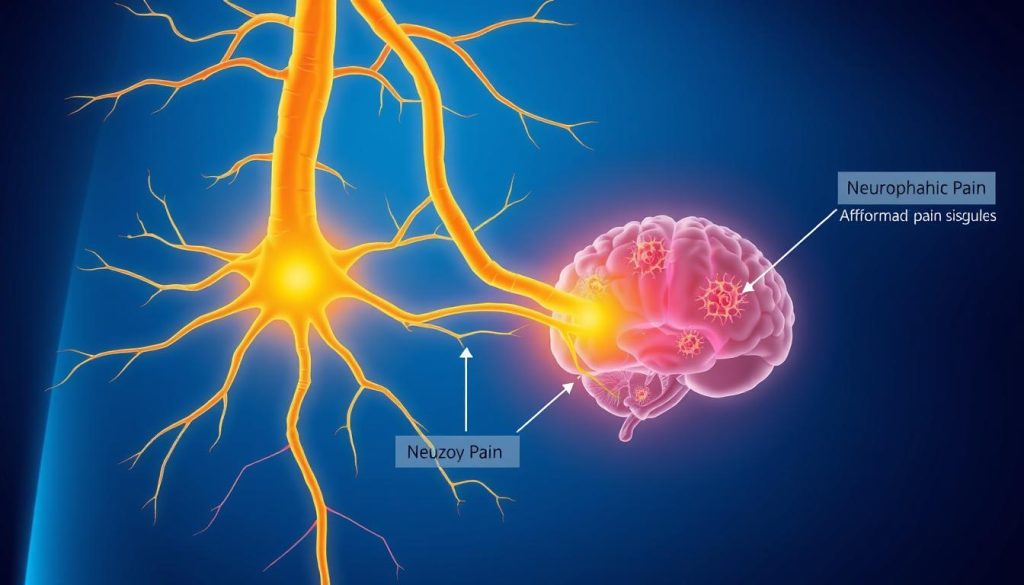
Neuropathic pain occurs when damaged nerves send incorrect pain signals to the brain
Try Pregablin 300mg
Published on: May 21, 2025
Last updated: January 28, 2026

